Natural Environment Land
The chapter “Natural Environment Land” from BOSEM class 7 social science chapter 2 is about the Earth’s structure and the various geological processes and features associated with it. It covers the following topics:
Earth’s Formation and Composition:
✔ Formation of the Earth and the appearance of modern humans.
✔ Earth’s interior structure, including the crust, mantle, and core.
✔ Seismic waves and their role in understanding the Earth’s interior.
Rocks and Minerals:
✔ Different types of rocks (igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic) and their formation.
✔Characteristics and examples of minerals.
Rock Cycle:
✔ The transformation process of rocks from one type to another through various geological processes.
Earth Movements:
✔ Internal (endogenic) forces and their impact, including earthquakes and volcanic activity.
✔ Classification of earth movements into sudden and slow movements.
Major Landforms:
Description of major landforms such as mountains, plateaus, and plains.
Different types of mountains and plateaus are based on their formation and location.
Processes of Weathering and Erosion:
The role of weathering and erosion in shaping the Earth’s surface.
Formation of sedimentary and metamorphic rocks through these processes.
Chapter Name: Natural Environment Land
Subject: Social Science
Lesson: 2
Class: 7
Board: Board Of Secondary Education Manipur (BOSEM/BSEM)
Contents: Questions and Answers, Explanation Video and notes
Table of Contents
Class 7 Social Science Chapter 2: Natural Environment-Land
Short notes
👉 The Earth, our homeland, is the third of the eight planets that orbit the sun. It is the only planet which supports life. It was formed from a cloud of gas and dust about 4,600 million years ago. Homo sapiens (modern humans) appeared on the earth about 2.5 lakh years ago.
👉 The most important source of the earth’s interior comes from seismic waves generated by earthquakes. They originate from the focus of the earthquake and travel in all directions. There are three types of waves known P waves (Primary waves), S waves (Secondary waves), and L waves (Long waves). S waves are transmitted only through a solid body.
👉 The interior of the earth consists of three concentric layers – the crust, the mantle, and the core. The crust is a thin, solid layer forming the outer shell of the earth. It includes continental crust and oceanic crust.
👉 A very thick layer called the mantle lies beneath the crust. It is composed of heavy rocks. The innermost part of the earth is known as the core. It is composed of iron and nickel. The inner core has a temperature of about 4000°C. Sometimes hot materials from the earth’s interior come out through cracks or joints as lava and form volcanoes.
👉The crust and topmost layer of the mantle form the lithosphere. The lithosphere consists of rigid plates bounded by oceanic ridges, trenches, and faults. There are seven very large plates and several smaller ones.
Rocks and minerals
👉The materials that make up the earth’s crust are called rocks. Examples are granite, sandstone, marble, clay, sand, salt, and coal. They do not possess a definite chemical composition but are a mixture of two or more minerals.
👉A mineral, on the other hand, has a definite chemical composition, a crystalline form, and certain physical properties. Examples are Silicates, quartz, common salt, etc.
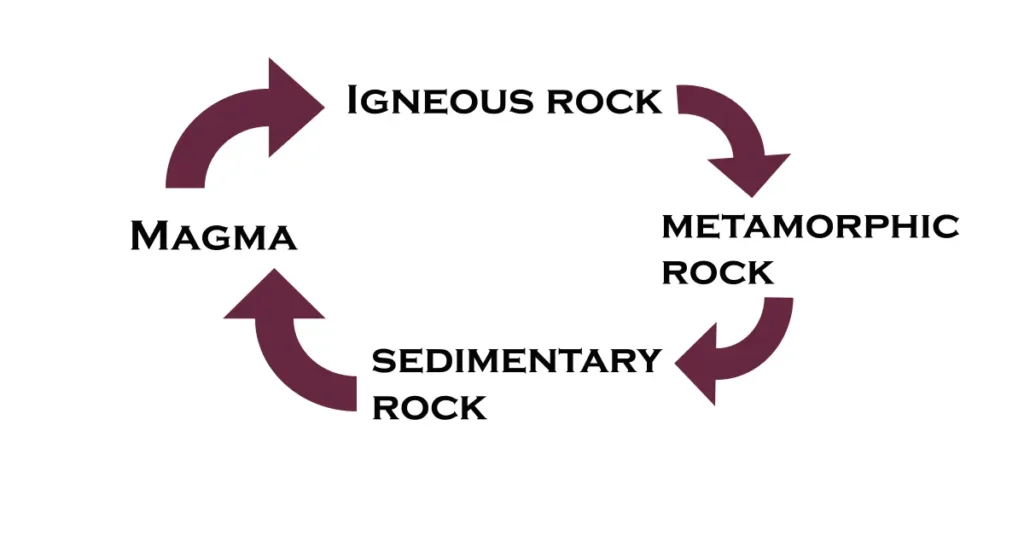
👉Based on their mode of formation, rocks are classified into three groups – igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic.
👉Igneous rocks are formed when molten rock called magma cools and solidifies. Igneous rocks are the parents of all other rocks and are also known as primary rocks.
👉Rivers and streams carry rock pieces and deposit as sediments which are buried layer by layer slowly. Due to pressure from above or because of cementation, the loose materials ultimately become sedimentary rocks e.g. sandstone, shale, limestone.
👉When the original character of the rocks, i.e., colour, hardness, and mineral composition is changed due to heat and pressure, it gives rise to metamorphic rocks. Examples are quartzite, marble, slate, and gneiss. The famous Taj Mahal in Agra is built of white marble.
👉Rock cycle: The process of transformation of rocks from one to another is known as the rock cycle.
👉Igneous rock is exposed to weathering and erosion and changed into sedimentary rocks. These two rocks are changed into metamorphic rocks in the course of time. The metamorphic rocks are forced deep into the earth’s interior and melted to form magma.
👉Earth movements: The forces which originate inside the earth and bring changes on the surface are known as Endogenous or Internal forces. The forces that work on the surface of the earth are called exogenic or external forces.
👉The Endogenic forces are divided into sudden and slow movements.
👉Sudden movements bring abrupt changes to the earth’s surface. Earthquakes and volcanic eruptions cause sudden movement in the earth’s crust.
👉Earthquake: Earthquakes are vibrations of the earth’s surface. The Richter scale (0-9) is used to measure the magnitude or strength of an earthquake.
👉Slow movements continue over long periods and bring about a change in the surface level of a place. Slow movements are further classified into vertical movements and horizontal movements.
👉Vertical movements are responsible for the rise or fall of a part of the earth’s surface. These earth movements built up continents.
👉Horizontal movements disturb the horizontal arrangement of rock layers. These movements are responsible for the formation of mountains.
Major Landforms: The major landforms of the earth are mountains, plateaus, and plains.
👉Mountains: A highland on the surface of the earth is called a mountain. When its summit is less than 900 meters from the base it is called a hill.
Mountains are classified into fold mountains e.g. the Himalayas, the Alps, the Andes, and the Aravallis.
Block Mountains e.g. the Vindhyas and the Satpuras.
Residual Mountains e.g. the Nilgiri Hills.
Volcanic Mountains e.g. Mt. Fuji Yama and Mt. Popa.
👉Plateaus: A plateau is an elevated area. It has a large summit with an even surface. Very often, rivers cut out deep valleys in a plateau region.
Based on their situation, there are three types of plateaus. They are:
(a) Intermontane plateaus which are enclosed by mountains,
(b) Piedmont plateaus that are situated at the foot of a mountain and
(c) Continental plateaus which rise abruptly from the lowlands or the sea.
👉Plains: A flat and low-lying land surface is called a plain. The uplift of a part of the sea floor forms uplifted coastal plains.
Erosional plains are formed when an elevated tract of land is worn down to a plain by erosion. Depositional plains are formed by the filling up of depressions with sediments.
Natural Environment Land questions and answers
Answer the following question in one word or sentence
Q1. Name the layer of the earth in which S wave cannot pass through.
Ans: The layer of the earth in which S wave cannot pass through is the core.
Q2. What type of form when lava solidify on the surface of the earth?
Ans: Igneous rock.
Q3. Which force is responsible for the folding of rock strata?
Ans: The compressional force is responsible for the folding of the rock strata.
Answer the following questions in about 40 words each
Q1. How are metamorphic rocks formed? Give two examples.
Ans: Metamorphic rocks are formed from existing rocks that undergo changes due to high heat, pressure, or chemically active fluids. This process, called metamorphism, alters the mineral composition and structure of the original rocks, transforming them into new types of rocks with different physical and chemical properties.
Two examples of metamorphic rock are marble and slate.
Q2. What is a rock cycle?
Ans; The process of transformation of the rock from one to another is known as the rock cycle.
Q3. What do you understand by Endogenic force?
Ans: The forces which originate inside the earth and bring changes on the surface of the earth are known as endogenic forces.
Q4. Differentiate between vertical and horizontal movements of the earth.
Ans:
| Vertical movement | Horizontal movement |
|---|---|
| These movements are responsible for the rise or fall of a part of the earth’s surface | Horizontal movements disturb the horizontal arrangement of rock layers |
| These movements build up the continent | These movements are responsible for the formation of the mountains. |
Choose the correct answer
1. Right valleys are formed between two
a) Fold Mountains
b) Block Mountains
c) Residual Mountains
d) Volcanic Mountains
Ans: Fold Mountains
2. The plateau which is enclosed by mountains is called
a) Continental plateau
b) Dissected Plateau
c) Piedmont Plateau
d) Intermontane Plateau
Ans: Intermontane Plateau
3. The Imphal valley is a lacustrine plain because it was formed due to
a) Erosion of a highland
b) Uplift of the sea floor
c) Sedimentation in a lake
d) Draining out of accumulated water.
Ans: Sedimentation in a lake.
Give the correct terms for the following
a) The place of origin of an earthquake inside the earth
Ans: Epicentre
b) The molten part of the upper mantle
Ans: Asthenosphere
c) Remains of plants and animals found in sedimentary rocks
Ans: Fossils
d) The fracture in rocks involving movement of strata
Ans: Faultiing
e) The upfolds of rock strata
Anticlines.




