The chapter “Getting To Know Plants” introduces students to the classification of plants based on their characteristics. Learn about herbs, shrubs, and trees, as well as creepers and climbers. The chapter also covers different parts of a plant, including roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and their respective functions. Concepts such as leaf venation, root systems, and the role of plants in the ecosystem are also explored.
Learning Objectives:
Important Terms and Definitions:
Solutions for Getting To Know Plants
Textbook Exercises
Q1. Correct the following statements and rewrite them in your notebook:
a. Stems absorb water and minerals from the soil.
Ans: Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil.
b. Leaves hold the plant upright
Ans: Stem holds the plant upright.
c. Roots conduct water to the leaves.
Ans: Stem conducts water to the leaves.
d. The number of petals and stamens in a flower is always equal.
Ans: The number of petals and stamens in a flower may not always be equal.
e. If the sepals of a flower are joined together, its petals are also joined together.
Ans: If the sepals of a flower are joined together, then its petals may or may not be joined together.
f. If the petals of a flower are joined together, then the pistil is joined to the petal.
Ans: If the petals of a flower are joined together, then the pistil may or may not be joined to the petal.
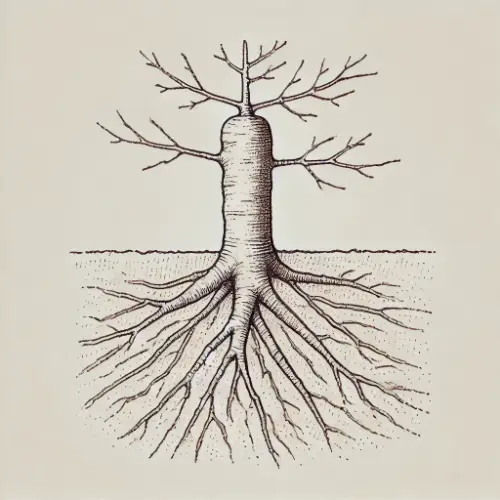
Q2. Draw a) A leaf (b) A taproot (c) A Flower.
Ans:
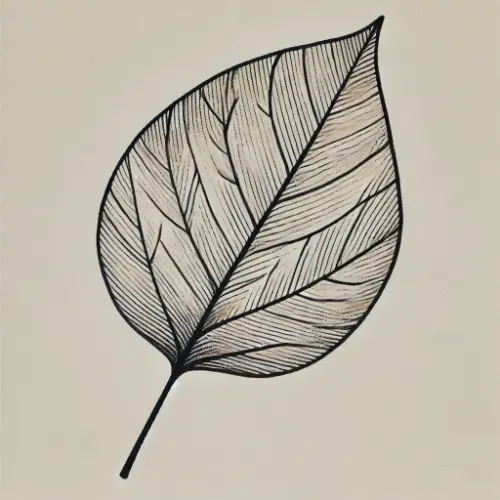
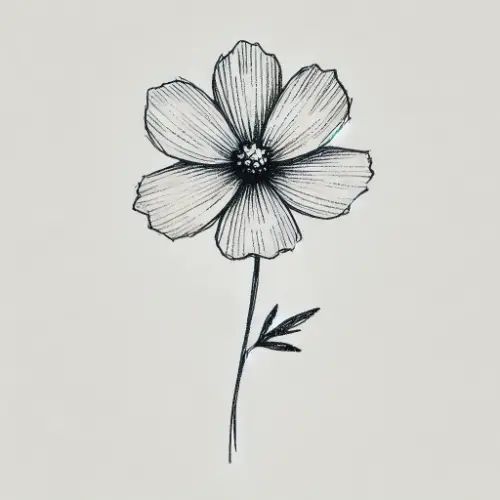


Q3. Can you find a plant in your house or in your neighbourhood which has a long but weak stem? Write its name. In which category will you place it?
Ans: Yes, the money plant has a long but weak stem. It comes under the category of climbers.
Q4. What is the function of a stem?
Ans: The function of a stem is to conduct water and minerals from the roots to the leaves and other parts of the plants.
Q5. Which of the following leaves has reticulate venation?
Wheat, Tulsi, Maize, Grass, Coriander and Chinarose.
Ans: Tulsi, Coriander and Chinarose have reticulate venation.
Watch this animation video about Venation
Q6. If a plant has fibrous roots, what type of venation do its leaves have?
Ans: The plants having fibrous roots will have parallel venation.
Q7. If a plant has leaves with reticulate venation, what kinds of roots will it have?
Ans: Plants having reticulate venation will have taproot.
Q8. Is it possible to find out whether a plant has fibrous roots or taproot by looking at the impression of its leaf on a sheet of paper?
Ans: Yes, it is possible. If a plant has a fibrous root then its leaves will have parallel venation, and if a plant has tap root then its leaves will have reticulate venation.
Q9. What are the parts of a flower?
Ans: The parts of a flower are
1. Sepal
2. Petal
3. Stamens and
4. Pistil.
Watch Parts of a flower Animation
Q10. From the following plants which of them has flowers?
| Grass | Maiz |
| Wheat | Chilli |
| Tomato | Tulsi |
| Pepal | Sheesham |
| Banyan | Mango |
| Jamun | Guava |
| Pomegranate | Papaya |
| Banana | Lemon |
| Sugarcane | Potato |
| Groundnut |
Ans: Chilli, Tomato, Tulsi, Mango, Jamun, Guava, Pomegranate, Papaya, Banana, Lemon.
Q11. Name the parts of a plant which produces food. Name the process.
Ans: Leaves are the part of a plant which produces food. The process is called photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis Animation
Q12. In which part of a flower, will you find the ovary?
Ans: We will find the ovary in the lowermost and the swollen part of the pistil.
Q13. Name two plants in which, one has joined sepals and the other has separated sepals.
Ans: Joined sepals: Periwinkle and Chinarose.
Separated sepals: Rose and Jasmine.
Getting to Know Plants Extra Questions and Answers
Q1. What is photosynthesis?
Ans: The process by which leaves make food for the plants in the presence of sunlight, water and carbon dioxide, is called photosynthesis.
Q2. Name the two main types of roots.
Ans: The two main types of roots are tap roots and fibrous roots.
Q3. What are tap roots and fibrous roots?
Ans: Tap roots are the single main root of a plant.
Fibrous roots do not have a main root but have a bunch of small similar roots.
Q4. Define Midrib.
Ans: A prominent line in the middle of a leaf is called a midrib.
Q5. What is leaf venation?
Ans: The design made by veins in a leaf is called leaf venation.
Q6. What is petiole?
Ans: The part of a leaf attached to the stem is called a petiole.
Q7. What are trees?
Ans: Trees are very tall, hard and thick-stem plants.
Example: Mango tree, Banayan tree, teak tree etc.
Q8. Difference between herbs and shrubs.
Ans:
| Herbs | Shrubs |
|---|---|
| Stems are green and tender | Stems are hard but not very thick |
| Usually short in height | Usually medium in height |
| May not have many branches | May have many branches near the base of the stem |
| Example: Grass, Mint, Corriander, Grass etc | Examples are rose, jasmine, hibiscus etc. |




